Difference between revisions of "Forward Calorimeter Expert"
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
==Checking Health Of Bases== | ==Checking Health Of Bases== | ||
| − | Maintaining a functioning FCAL with optimal health requires collecting | + | Maintaining a functioning FCAL with optimal health requires collecting monitoring HV and status values for each base and finding any bases outside of some specified range. This is accomplished using the following script: |
1. Login as hdops to any gluon computer | 1. Login as hdops to any gluon computer | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
5. Run the function "scan_monitoring(TString readback = ":status/:vmon", TString inequality = ">/</=", double Value = 0, bool compareSetpoint = false)" | 5. Run the function "scan_monitoring(TString readback = ":status/:vmon", TString inequality = ">/</=", double Value = 0, bool compareSetpoint = false)" | ||
| − | The scan_monitoring function was designed to be flexible but it does require some explanation, | + | The scan_monitoring function was designed to be flexible but it does require some explanation, as given below: |
| − | First, a text file is generated with 2800 lines with the pvName in column 1 and the value in column 2, where pvName is in the form FCAL:hv:Col:Row:readback. The text file is then parsed and compared to | + | First, a text file is generated with 2800 lines with the pvName in column 1 and the value in column 2, where pvName is in the form FCAL:hv:Col:Row:readback. The text file is then parsed and compared to "Value" yielding a true/false condition depending on "inequality". pvNames that pass this condition are printed to the screen. |
| − | The parameter "compareSetpoint" will compare the measured HV with the set HV and if the absolute difference is greater that the parameter "Value" then it is printed to the screen. | + | The parameter "compareSetpoint" will compare the measured HV with the set HV and if the absolute difference is greater that the parameter "Value" then it is printed to the screen. These are the only parameters that matter in this case. |
Readback can take any suffix used by epics to tag the type of base response. The list of possible variables monitored by epics are: | Readback can take any suffix used by epics to tag the type of base response. The list of possible variables monitored by epics are: | ||
* :v0set = this is NOT a variable that comes from the base BUT a something you can set in epics and is reset to 0 every time the IOC reboots | * :v0set = this is NOT a variable that comes from the base BUT a something you can set in epics and is reset to 0 every time the IOC reboots | ||
| − | * :status = is 0 or 1 depending if the base is disabled or enabled | + | * :status = is 0 or 1 depending if the base is disabled or enabled, respectively |
* :vmon = measured HV | * :vmon = measured HV | ||
* :imon = measured Current | * :imon = measured Current | ||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
* :mvb = The average voltage supplied to the bottom half of pins is called Medium Voltage Bottom | * :mvb = The average voltage supplied to the bottom half of pins is called Medium Voltage Bottom | ||
* :mvt = The average voltage supplied to the top half of pins is called Medium Voltage Top | * :mvt = The average voltage supplied to the top half of pins is called Medium Voltage Top | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Examples: | Examples: | ||
Revision as of 10:23, 28 October 2014
Contents
For Expert Only!!
Brief overview of electronics
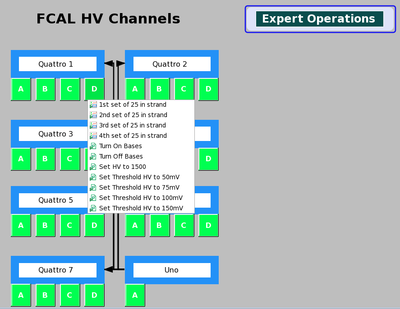
There are 7 anagate Quattros, and 4 power chassis. Each anagate has 4 ports labeled A, B, C, D in the Expert GUI. Each power chassy can be broken up into a left and right half with 4 power supplies in each half. The power supplies in each half can be power cycled by an anagate via an I/O cable. Not all cables were made properly so a few busses will not power cycle, tests still need to be done to find which busses this affects.
The Expert GUI
Looking at the FCAL by anagate Quattro and ports can help troubleshoot problems common to bases on a strand. The GUI shown in Figure 1 shows the 7 Quattro as they would look like on the FCAL platform. From this GUI one can enable the HV to bases on a strand or quattro level. At the moment power cycling is not integrated into EPICS so read the next section for instructions.
Power cycling a bus
To power cycle a bus do the following:
1. Login as hdops on any gluon computer
2. Go to "/gluonfs1/gluex/Subsystems/FCAL/manny_scripts/temp/newBaseControl" and type "source setup"
3. Type "pChControl"
4. Type "5" Write Anagate Digital
5. Select the Quattro number as shown in Figure 1
6. Select the Port to power cycle
Rebooting the IOC
If a base needs to have its HV disabled and you are unable to do so from the GUI you may need to reboot the IOC. To do this:
1. Login to gluon30 with hdops
2. Connect the to the IOC by entering "telnet localhost 27000" on the command line
3. To reboot the IOC enter "ctrl + x". The IOC will take a few minutes to reconnect
4. To exit the IOC enter "ctrl + ]" and then "quit"
Checking Health Of Bases
Maintaining a functioning FCAL with optimal health requires collecting monitoring HV and status values for each base and finding any bases outside of some specified range. This is accomplished using the following script:
1. Login as hdops to any gluon computer
2. Go to "/gluonfs1/gluex/Subsystems/FCAL/FCAL_Analysis/scripts"
3. Type "root -l setup.C"
4. Type ".L EpicsMonitoring.C++"
5. Run the function "scan_monitoring(TString readback = ":status/:vmon", TString inequality = ">/</=", double Value = 0, bool compareSetpoint = false)"
The scan_monitoring function was designed to be flexible but it does require some explanation, as given below:
First, a text file is generated with 2800 lines with the pvName in column 1 and the value in column 2, where pvName is in the form FCAL:hv:Col:Row:readback. The text file is then parsed and compared to "Value" yielding a true/false condition depending on "inequality". pvNames that pass this condition are printed to the screen.
The parameter "compareSetpoint" will compare the measured HV with the set HV and if the absolute difference is greater that the parameter "Value" then it is printed to the screen. These are the only parameters that matter in this case.
Readback can take any suffix used by epics to tag the type of base response. The list of possible variables monitored by epics are:
- :v0set = this is NOT a variable that comes from the base BUT a something you can set in epics and is reset to 0 every time the IOC reboots
- :status = is 0 or 1 depending if the base is disabled or enabled, respectively
- :vmon = measured HV
- :imon = measured Current
- :dyn = measured Dynode HV
- :dac = Digital Analog Converter used by the base to set a HV
- :mvb = The average voltage supplied to the bottom half of pins is called Medium Voltage Bottom
- :mvt = The average voltage supplied to the top half of pins is called Medium Voltage Top
Examples:
1. To find all bases whose HV is disabled do type the following:
scan_monitoring(":status","=",0,false)
2. To find all bases whose measured HV is greater than 2000 Volts do the following:
scan_monitoring(":vmon",">",2000,false)
3. To find all bases where the absolute difference between the measured and set HV is greater than 300 do the following: (The readback and inequality parameter are irrelevant when "compareSetpoint" is true)
scan_monitoring("","",300,true)