Difference between revisions of "High Intensity Running"
From GlueXWiki
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Reference Material == | == Reference Material == | ||
| − | * [[Media:20160722_L3status.pdf|L3 | + | * [[Media:20160722_L3status.pdf|L3 mini-review Slides (7/22/2016 )]] |
* [[Level-3 Trigger Meetings]] | * [[Level-3 Trigger Meetings]] | ||
* [[Media:2007-08-29_VME_DAQ_Rates.pdf|Constraints from VME and Network Interfaces]] | * [[Media:2007-08-29_VME_DAQ_Rates.pdf|Constraints from VME and Network Interfaces]] | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
# L1 trigger | # L1 trigger | ||
## What is a reasonable ratio of various trigger types at high intensity? | ## What is a reasonable ratio of various trigger types at high intensity? | ||
| − | ## What is the L1 trigger rate expected for the 50 MHz beam, extrapolating the Spring 2016 conditions: the FCAL+BCAL trigger? other triggers? The accidentals should be considered. | + | ## '''What is the L1 trigger rate expected for the 50 MHz beam, extrapolating the Spring 2016 conditions: the FCAL+BCAL trigger? other triggers? The accidentals should be considered.''' |
## What is the relative drop of the trigger efficiency for a twice more stringent FCAL+BCAL trigger, which would leave 50% of the events of the 2016 Spring run? | ## What is the relative drop of the trigger efficiency for a twice more stringent FCAL+BCAL trigger, which would leave 50% of the events of the 2016 Spring run? | ||
## Would a ST*(FCAL+BCAL), or other coincidence help to reduce the trigger rate minimizing the efficiency loss? | ## Would a ST*(FCAL+BCAL), or other coincidence help to reduce the trigger rate minimizing the efficiency loss? | ||
Revision as of 11:44, 15 August 2016
Overview
This page gathers information related to high intensity (5 x 107 γ/s - 50 MHz in 8.4-9.0 GeV) GlueX running.
Reference Material
- L3 mini-review Slides (7/22/2016 )
- Level-3 Trigger Meetings
- Constraints from VME and Network Interfaces
- Flux: evaluation of the photon flux for Spring 2016 - 10Mhz (8.4-9.0 GeV) with the old "50 µm" diamond, PERP mode, 5mm collimator, beam 130µA
Planning
Near-term Questions
Here is a place to gather some questions that need to be answered in order to properly plan for high intensity running.
- L1 trigger
- What is a reasonable ratio of various trigger types at high intensity?
- What is the L1 trigger rate expected for the 50 MHz beam, extrapolating the Spring 2016 conditions: the FCAL+BCAL trigger? other triggers? The accidentals should be considered.
- What is the relative drop of the trigger efficiency for a twice more stringent FCAL+BCAL trigger, which would leave 50% of the events of the 2016 Spring run?
- Would a ST*(FCAL+BCAL), or other coincidence help to reduce the trigger rate minimizing the efficiency loss?
- DAQ
- How do the event sizes scale with the beam intensity (for the triggers used)?
- What are the expected data rates for each crate?
- How do the data rates scale with beam intensity?
- Can we reduce the data read from each crate by dropping headers or reformatting? (e.g. fADC125 Trigger Times)
- Can we reduce the data read from each crate by reducing readout windows?
- Do the tagger data rates really drop below the FDC when the windows are reduced?
- What is the real limit on the VME data transfer speed considering the bus clocks and the duty cycles provided by various modules?
- What crates (FDC?) would limit the DAQ capabilities at the VME transfer level?
- What crates would limit the DAQ capabilities at the Ethernet level? What gain a 10 Gb interface would provide?
- L3
- What would be the largest reduction factor at "high intensity" (long events), if no time limit is considered?
- How many nodes are needed for a reduction factors of 4 at a 100 kHz event rate?
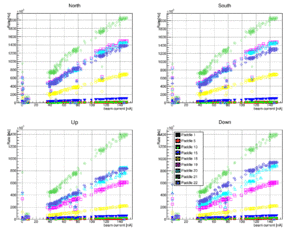
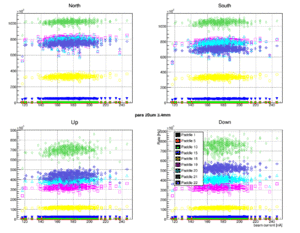
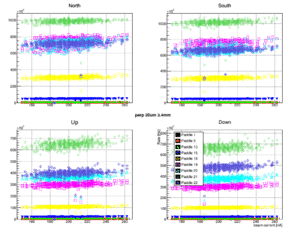
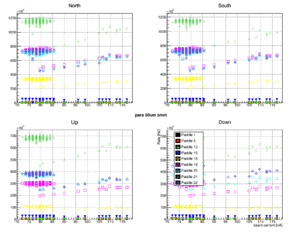
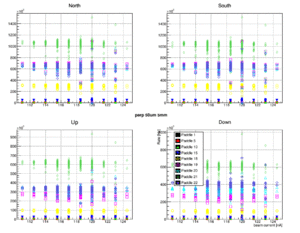
TOF
rates for PMTs of selected paddles, paddle 1 to 19 are regular width/length paddles, paddle 20 and 21 are narrow width long paddles and paddle 22 is a short single ended paddle. The rates are in Hz as a function of beam current in nA. The data are from runs 11634 to 11637 where luminosity scans were done from 40 to 140nA. The collimator was set to 5mm diameter and the radiator is 3x10-4 with LH target full.