Difference between revisions of "Parameterization of deflections/preliminary momentum resolution results"
From GlueXWiki
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
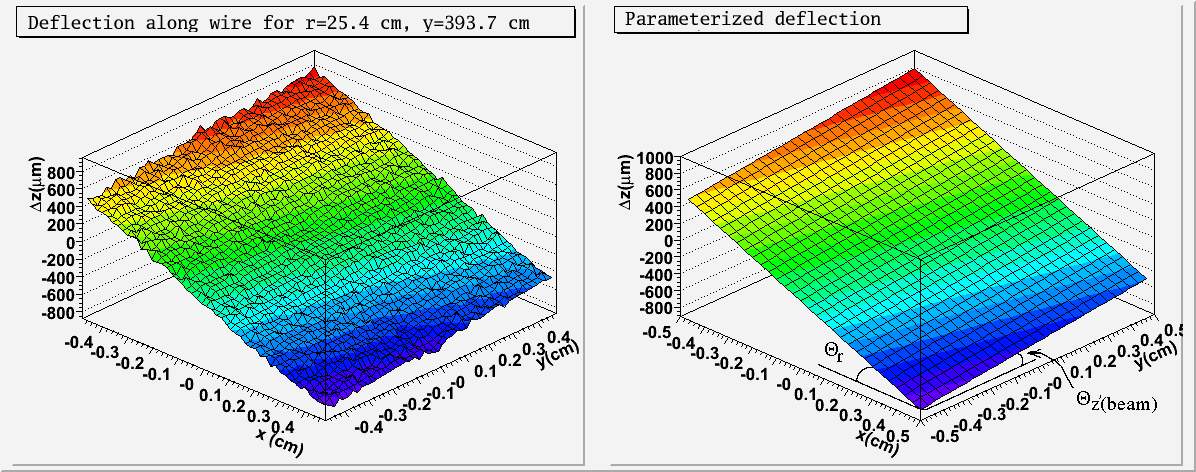
Using the 1500 Amp TOSCA map provided by Paul Brindza, I ran Garfield calculations over a grid in z and r corresponding to the dimensions of the FDC to compute the deflections of the avalanches along the wire due to the Lorentz force. The behavior of this deflection for ionizations throughout a given | Using the 1500 Amp TOSCA map provided by Paul Brindza, I ran Garfield calculations over a grid in z and r corresponding to the dimensions of the FDC to compute the deflections of the avalanches along the wire due to the Lorentz force. The behavior of this deflection for ionizations throughout a given | ||
| − | FDC cell is well-described by a plane | + | FDC cell is well-described by a plane: |
[[Image:deflection_example.gif]] | [[Image:deflection_example.gif]] | ||
Revision as of 09:50, 22 May 2007
Using the 1500 Amp TOSCA map provided by Paul Brindza, I ran Garfield calculations over a grid in z and r corresponding to the dimensions of the FDC to compute the deflections of the avalanches along the wire due to the Lorentz force. The behavior of this deflection for ionizations throughout a given FDC cell is well-described by a plane:
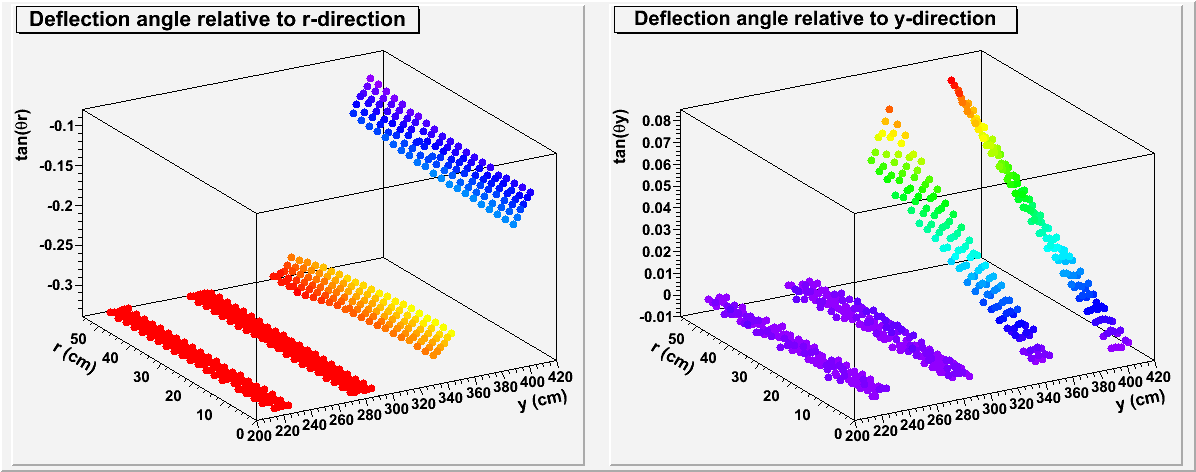
The two slope (tangent) parameters describing the deflection planes are shown as a function of r and z(beam direction) here:
The hitFDC.c routine in HDGeant has been modified to read in a table of these tangent values and interpolate the amount of deflection as a function of the point of closest approach to the avalanche wire on a wire-by-wire/event-by-event basis.